优秀!这个开源项目中基于Redisson封装了CacheManager的缓存实现
RuoYi-Vue-Plus 是针对 RuoYi-Vue 进行了相关的重写,针对分布式集群场景全方位升级(不兼容原框架)的一个后端快速开发框架。RuoYi-Vue-Plus项目目前也加入了dromara开源社区。为啥我想介绍这个后端快速开发平台呢?在项目根目录下的ruoyi-framework工程下的src的源码包com.ruoyi.framework.manager中,存在这样一个类:ini复制
一、背景
作为一名Java后端开发工程师,日常写Redis缓存的操作的类,可能大部分场景下用的都是RedisTemplate的设计和实现,与CacheManager这种注解集成后,也会用它作为实现,那么今天我给大家分享一种最近学习到的设计和实现,他来自于开源项目中的的代码,基于Redisson这种封装了CacheManager的实现,替换了RedisTemplate,感兴趣的可以尝试试用下,这样就不必为了jedis还是luttuce的redistemplate切换问题头疼了。
二、RuoYi-Vue-Plus介绍
RuoYi-Vue-Plus 是针对 RuoYi-Vue 进行了相关的重写,针对 分布式集群 场景全方位升级(不兼容原框架)的一个后端快速开发框架。
开源主页地址:gitee.com/dromara/Ruo…
RuoYi-Vue-Plus项目目前也加入了dromara开源社区。
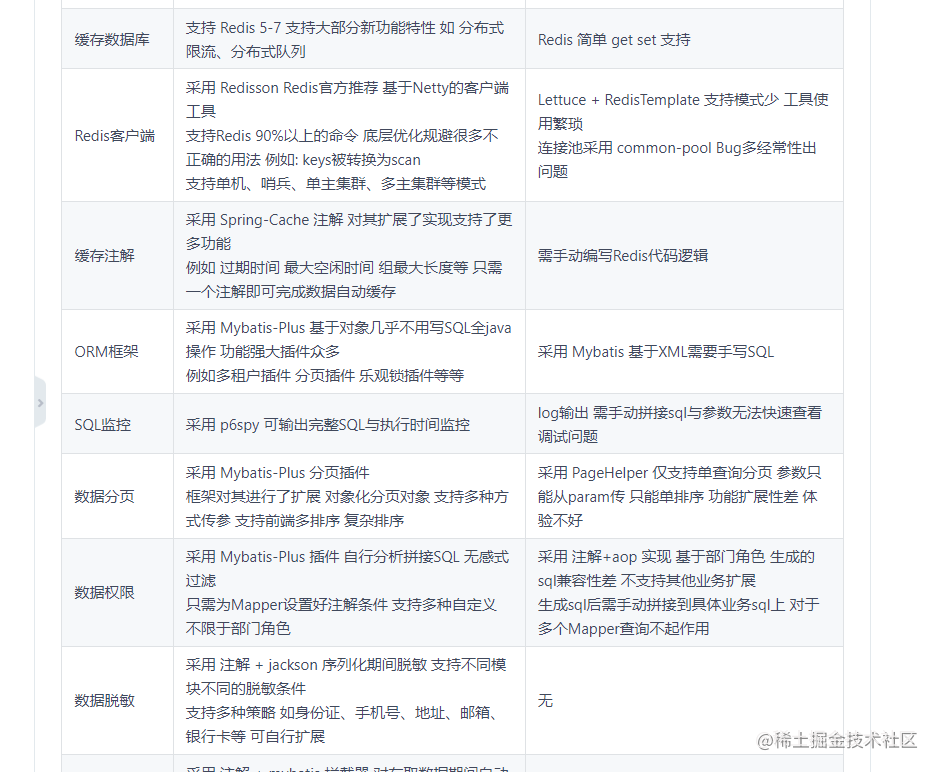
为啥我想介绍这个后端快速开发平台呢?因为最近在做公司项目的时候,需要进行某项业务需求的快速环境搭建和开发,同时做些技术上的升级和预研,所以这里选择了这个,虽然他是一个后端CRUD类型的管理端的平台,但是某些小的设计思想和实现也是可以学习的,毕竟老是用一种后端框架去做业务开发,多少会把自己限制死吧,多多去新世界了解一下玩法还是不错的,这个框架和原始ruoyi的区别如下:

三、基于Redisson封装的CacheManager
这个项目中采用了Redisson(基于Netty的客户端工具 ),据说支持Redis 90%以上的命令等
并采用 了Spring-Cache 注解 对其扩展了实现支持了更多功能,例如:
过期时间
最大空闲时间
组最大长度等
只需一个注解即可完成数据自动缓存
3.1、PlusSpringCacheManager类定义
在项目根目录下的ruoyi-framework工程下的src的源码包com.ruoyi.framework.manager中,存在这样一个类:
ini
复制代码
package com.ruoyi.framework.manager; import com.ruoyi.common.utils.redis.RedisUtils; import org.redisson.api.RMap; import org.redisson.api.RMapCache; import org.redisson.spring.cache.CacheConfig; import org.redisson.spring.cache.RedissonCache; import org.springframework.boot.convert.DurationStyle; import org.springframework.cache.Cache; import org.springframework.cache.CacheManager; import org.springframework.cache.transaction.TransactionAwareCacheDecorator; import org.springframework.util.StringUtils; import java.util.Collection; import java.util.Collections; import java.util.Map; import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap; import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentMap; /** * A {@link org.springframework.cache.CacheManager} implementation * backed by Redisson instance. * <p> * 修改 RedissonSpringCacheManager 源码 * 重写 cacheName 处理方法 支持多参数 * */ @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public class PlusSpringCacheManager implements CacheManager { private boolean dynamic = true; private boolean allowNullValues = true; private boolean transactionAware = true; Map<String, CacheConfig> configMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(); ConcurrentMap<String, Cache> instanceMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(); /** * Creates CacheManager supplied by Redisson instance */ public PlusSpringCacheManager() { } /** * Defines possibility of storing {@code null} values. * <p> * Default is <code>true</code> * * @param allowNullValues stores if <code>true</code> */ public void setAllowNullValues(boolean allowNullValues) { this.allowNullValues = allowNullValues; } /** * Defines if cache aware of Spring-managed transactions. * If {@code true} put/evict operations are executed only for successful transaction in after-commit phase. * <p> * Default is <code>false</code> * * @param transactionAware cache is transaction aware if <code>true</code> */ public void setTransactionAware(boolean transactionAware) { this.transactionAware = transactionAware; } /** * Defines 'fixed' cache names. * A new cache instance will not be created in dynamic for non-defined names. * <p> * `null` parameter setups dynamic mode * * @param names of caches */ public void setCacheNames(Collection<String> names) { if (names != null) { for (String name : names) { getCache(name); } dynamic = false; } else { dynamic = true; } } /** * Set cache config mapped by cache name * * @param config object */ public void setConfig(Map<String, ? extends CacheConfig> config) { this.configMap = (Map<String, CacheConfig>) config; } protected CacheConfig createDefaultConfig() { return new CacheConfig(); } @Override public Cache getCache(String name) { // 重写 cacheName 支持多参数 String[] array = StringUtils.delimitedListToStringArray(name, "#"); name = array[0]; Cache cache = instanceMap.get(name); if (cache != null) { return cache; } if (!dynamic) { return cache; } CacheConfig config = configMap.get(name); if (config == null) { config = createDefaultConfig(); configMap.put(name, config); } if (array.length > 1) { config.setTTL(DurationStyle.detectAndParse(array[1]).toMillis()); } if (array.length > 2) { config.setMaxIdleTime(DurationStyle.detectAndParse(array[2]).toMillis()); } if (array.length > 3) { config.setMaxSize(Integer.parseInt(array[3])); } if (config.getMaxIdleTime() == 0 && config.getTTL() == 0 && config.getMaxSize() == 0) { return createMap(name, config); } return createMapCache(name, config); } private Cache createMap(String name, CacheConfig config) { RMap<Object, Object> map = RedisUtils.getClient().getMap(name); Cache cache = new RedissonCache(map, allowNullValues); if (transactionAware) { cache = new TransactionAwareCacheDecorator(cache); } Cache oldCache = instanceMap.putIfAbsent(name, cache); if (oldCache != null) { cache = oldCache; } return cache; } private Cache createMapCache(String name, CacheConfig config) { RMapCache<Object, Object> map = RedisUtils.getClient().getMapCache(name); Cache cache = new RedissonCache(map, config, allowNullValues); if (transactionAware) { cache = new TransactionAwareCacheDecorator(cache); } Cache oldCache = instanceMap.putIfAbsent(name, cache); if (oldCache != null) { cache = oldCache; } else { map.setMaxSize(config.getMaxSize()); } return cache; } @Override public Collection<String> getCacheNames() { return Collections.unmodifiableSet(configMap.keySet()); } }
代码中的:
scss
复制代码
RedisUtils.getClient()
代表的就是当前工程中的Redisson对象。
通过实现了标准的CacheManager接口,实现了一套缓存注解的实现类。
这个类本质上和Redisson包中自带的RedissonSpringCacheManager是同一份实现,但是这个开源项目中做了一点点的改变。支持了一下在注解中声明一种使用的约定,解析其约定的过期时间和空闲时间,作为参数
3.2、定义配置Bean
如果需要使用,则可以在项目的自动配置中进行声明:
csharp
复制代码
/** * 自定义缓存管理器 整合spring-cache */ @Bean public CacheManager cacheManager() { return new PlusSpringCacheManager(); }
3.3、项目中使用
开源项目中介绍的使用方式如下:
可以在使用时定义如下的Key格式:
cacheNames#ttl#maxIdleTime#maxSize
ttl:过期时间 如果设置为0则不过期 默认为0
maxIdleTime:最大空闲时间 根据LRU算法清理空闲数据 如果设置为0则不检测 默认为0
maxSize:组最大长度 根据LRU算法清理溢出数据 如果设置为0则无限长 默认为0
具体样例如下:
ini
复制代码
public class CacheNames { /** * 演示案例 */ String DEMO_CACHE = "demo:cache#60s#10m#20"; /** * 用户账户 */ String SYS_USER_NAME = "sys_user_name#30d"; /** * 部门 */ String SYS_DEPT = "sys_dept#30d"; /** * OSS内容 */ String SYS_OSS = "sys_oss#30d"; }
然后再相关的查询类的方法上增加注解进行缓存设置和缓存清除:
ini
复制代码
@Cacheable(cacheNames = CacheNames.SYS_DEPT, key = "#deptId") @Override public SysDept selectDeptById(Long deptId) { SysDept dept = baseMapper.selectById(deptId); if (ObjectUtil.isNull(dept)) { return null; } SysDept parentDept = baseMapper.selectOne(new LambdaQueryWrapper<SysDept>() .select(SysDept::getDeptName).eq(SysDept::getDeptId, dept.getParentId())); dept.setParentName(ObjectUtil.isNotNull(parentDept) ? parentDept.getDeptName() : null); return dept; } @CacheEvict(cacheNames = CacheNames.SYS_DEPT, key = "#dept.deptId") @Override public int updateDept(SysDept dept) { SysDept newParentDept = baseMapper.selectById(dept.getParentId()); SysDept oldDept = baseMapper.selectById(dept.getDeptId()); if (ObjectUtil.isNotNull(newParentDept) && ObjectUtil.isNotNull(oldDept)) { String newAncestors = newParentDept.getAncestors() + StringUtils.SEPARATOR + newParentDept.getDeptId(); String oldAncestors = oldDept.getAncestors(); dept.setAncestors(newAncestors); updateDeptChildren(dept.getDeptId(), newAncestors, oldAncestors); } int result = baseMapper.updateById(dept); if (UserConstants.DEPT_NORMAL.equals(dept.getStatus()) && StringUtils.isNotEmpty(dept.getAncestors()) && !StringUtils.equals(UserConstants.DEPT_NORMAL, dept.getAncestors())) { // 如果该部门是启用状态,则启用该部门的所有上级部门 updateParentDeptStatusNormal(dept); } return result; }
3.4、使用效果
这样设置以后,在redis中它会进行一个hash结构的存储,然后同一个缓存key的多个值,用一个redis的hash结构中的多个key来实现,它会通过一些后台的线程去维护和实现指定时间的缓存过期对象的淘汰等
3.5、跟着ChatGPT学一下
我们也来问问ChatGPT,让他给我们分析下吧。
问题1:
你现在是一名Java技术专家,请帮忙分析并回答下这个问题:Redisson中的缓存操作类和RedisTemplate的区别是什么?优势是什么?性能有多少提高?RedissonSpringCacheManager这个类操作Redis中的缓存怎么样
ChatGPT回答:
Redisson是一个基于Redis的Java客户端,提供了丰富的功能和API,包括缓存操作类。而RedisTemplate是Spring提供的对Redis的操作模板类。
区别:
-
功能和API:Redisson提供了更丰富的功能和API,除了基本的缓存操作外,还支持分布式锁、分布式集合、分布式对象等功能。而RedisTemplate主要关注于对Redis的基本操作,如字符串、哈希、列表等数据结构的操作。
-
使用方式:Redisson通过自己的API和注解来进行缓存操作,使用起来更加简单和方便。而RedisTemplate需要编写自定义的代码来操作Redis缓存。
优势:
-
分布式支持:Redisson提供了分布式锁、分布式集合等功能,可以方便地在分布式环境中使用。RedisTemplate在分布式场景下需要自己处理分布式锁等问题。
-
易用性:Redisson的API和注解设计简洁,使用起来更加方便。RedisTemplate需要编写更多的自定义代码来完成相同的操作。
性能提升:
Redisson通过优化网络通信和使用异步操作等技术手段,可以提高性能并减少资源消耗。具体的性能提升取决于具体的使用场景和操作方式,一般情况下Redisson相对于RedisTemplate会有一定的性能提升。
关于RedissonSpringCacheManager类,它是Redisson提供的与Spring Cache集成的类,用于操作Redis缓存。它通过实现Spring Cache的CacheManager接口,提供了与Spring框架集成的缓存操作功能。使用RedissonSpringCacheManager可以方便地使用Redisson来管理和操作Redis缓存,提供了更丰富的功能和更好的性能。具体的使用方法可以参考Redisson的官方文档和示例。
问题2:
那你能给我讲解下刚才这个问题中的RedissonSpringCacheManager类怎么使用吗
当使用RedissonSpringCacheManager类时,需要进行以下步骤:
-
添加Redisson和Spring Cache依赖:在项目的构建配置文件(如pom.xml)中添加Redisson和Spring Cache的依赖。
-
配置Redis连接信息:在项目的配置文件(如application.properties或application.yml)中配置Redis连接信息,包括主机名、端口、密码等。
-
创建RedissonSpringCacheManager Bean:在Spring配置文件中创建RedissonSpringCacheManager的Bean,并注入RedissonClient实例。
@Configuration public class CacheConfig {
typescript复制代码
@Bean public RedissonSpringCacheManager cacheManager(RedissonClient redissonClient) { return new RedissonSpringCacheManager(redissonClient, "classpath:/cache-config.yaml"); }}
上述示例中,使用RedissonClient和缓存配置文件创建了RedissonSpringCacheManager的Bean。缓存配置文件(cache-config.yaml)可以指定缓存的过期时间、缓存名称等配置信息。
-
在需要使用缓存的方法上添加注解:在需要使用缓存的方法上添加Spring Cache的注解,如
@Cacheable、@CachePut、@CacheEvict等。@Service public class MyService {
typescript复制代码
@Cacheable(value = "myCache", key = "#id") public Object getCachedData(String id) { // 从数据库或其他数据源获取数据 return data; }}
上述示例中,使用@Cacheable注解将方法的返回值添加到名为"myCache"的缓存中,缓存的键值为方法的参数id。
通过以上步骤,就可以使用RedissonSpringCacheManager类来操作Redis缓存。它会根据注解的配置自动从缓存中获取数据或将数据存入缓存,并提供了与Spring Cache集成的功能,如缓存过期、缓存清除等。
需要注意的是,具体的配置和使用方式可能会因项目的具体情况而有所不同,可以根据实际需求和官方文档进行进一步的配置和调整。
四、最后
日常开发工作中,我们可以通过大量阅读开源项目的代码来提高我们的技术能力、广度能力,不一定是天天看优秀的知名开源框架,有些解决了我们一些实际问题的项目代码也是值得我们学习的,说不定哪个类就可以在当前项目使用到了。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献3条内容
已为社区贡献3条内容










所有评论(0)